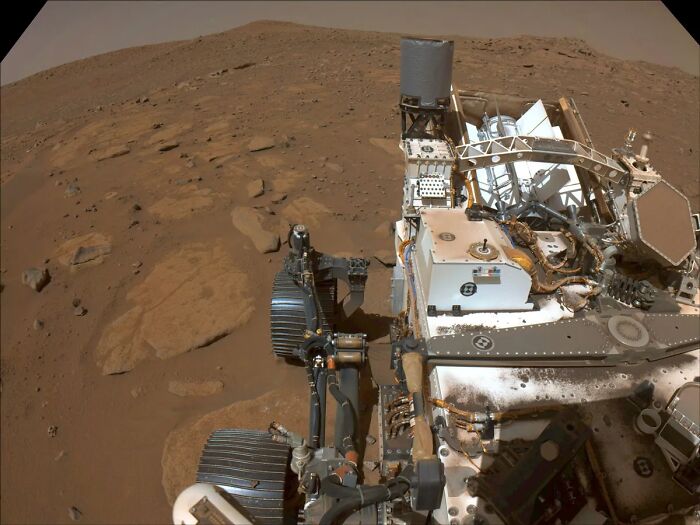
NASA’s Perseverance rover, better known as Percy, was designed to explore Jezero Crater on Mars as part of NASA’s Mars 2020 mission. It successfully landed on the Red Planet on February 18, 2021 and has been providing scientists with crucial information ever since.
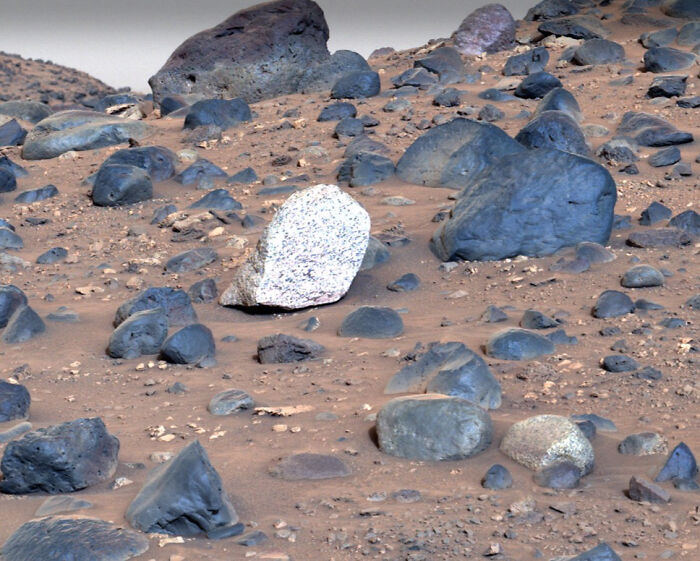
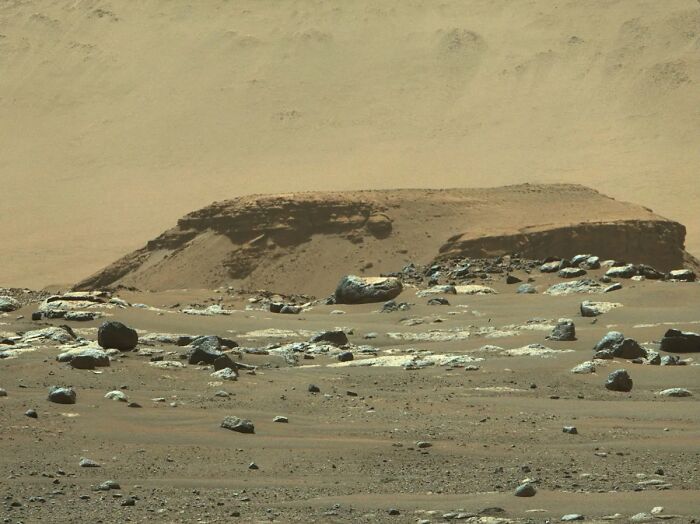
Recently, the rover has attracted immense scientific interest because it spotted something truly exciting and unusual: a one-of-a-kind white rock sitting on the surface of Mount Washburn, inside the massive Jezero Crater.
More information: NASA
NASA’s Perseverance rover, on Mars since February 2021, recently discovered a one-of-a-kind rock called Atoko Point.
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
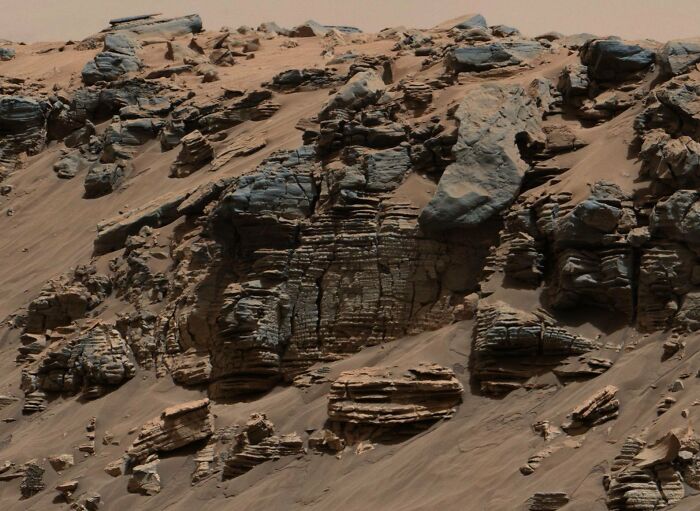
Images of the bright rock with dark spots reached scientists on May 27, 2024, the 1,162nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The 18-by-14-inch (45-by-35-centimeter) rock, because of its uniqueness, was named “Atoko Point” after the eastern Grand Canyon.
Analysis by Perseverance’s SuperCam and Mastcam-Z showed that Atoko Point is composed of minerals such as pyroxene and feldspar.
“In terms of the size, shape and arrangement of its mineral grains and crystals – and potentially its chemical composition – Atoko Point is in a league of its own,” NASA explained in its press release.
“The diversity of textures and compositions of Mount Washburn was an exciting discovery for the team, because these rocks represent a set of geological gifts brought from the crater rim and potentially beyond,” added Brad Garczynski of the University Western Washington, co-leader of the research team.
While the rock attracts attention for its appearance and chemical composition, the scientific team is also trying to determine where Atoko Point came from, and it appears that at present there are at least two different hypotheses.
One group of researchers suggests that Atoko Point was created in an underground body of magma that may now be exposed on the crater rim and the other part of the team believes the rock was created well beyond crater walls 28 miles wide. Jezero and was transported there by the “swift Martian waters” ages ago.
“Regardless, the team believes that while Atoko is the first of its kind they have seen, it will not be the last,” NASA said.
The unusual rock was discovered on the surface of Mount Washburn, a hill inside Jezero Crater.
Image credits: NASA
Photo credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
The primary goal of the Perseverance mission to Mars is astrobiology, searching for signs of ancient life and collecting rock and regolith samples for eventual return to Earth.
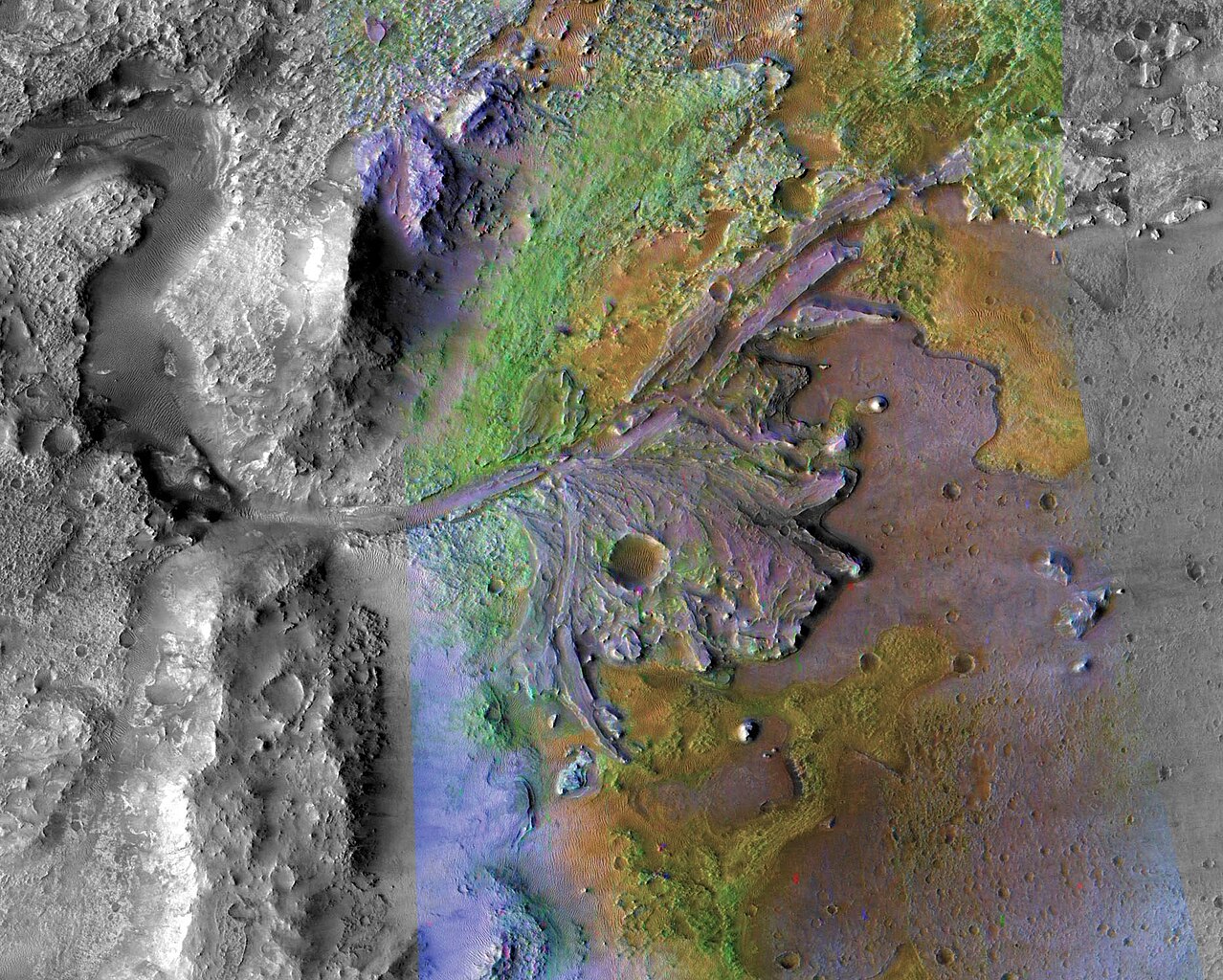
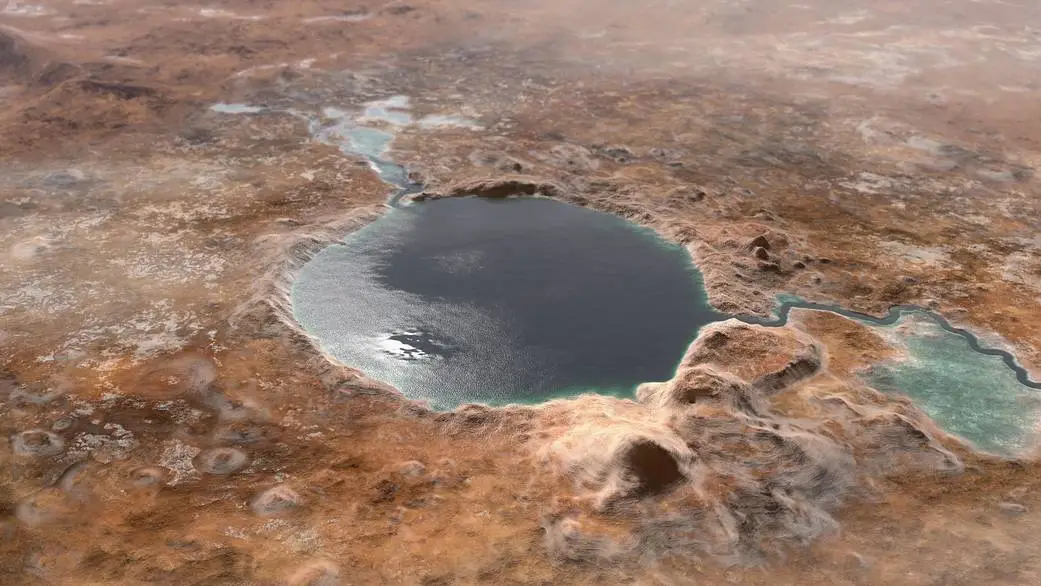
NASA’s Perseverance rover is studying Jezero Crater, a huge region on the Red Planet where ancient environments may have created the perfect conditions for microbial life. Equipped with a new subsystem for collecting Martian rock samples, Percy could provide possible evidence of past life.
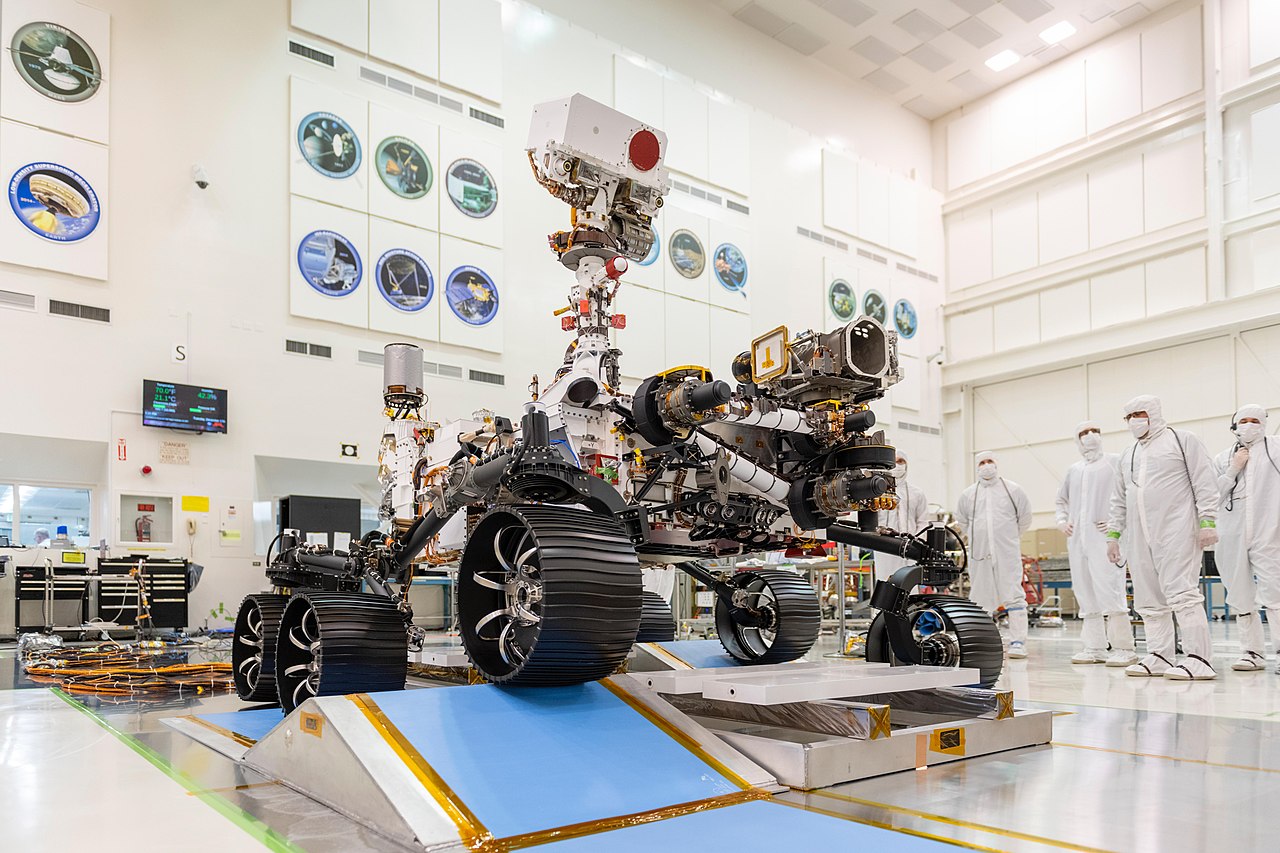
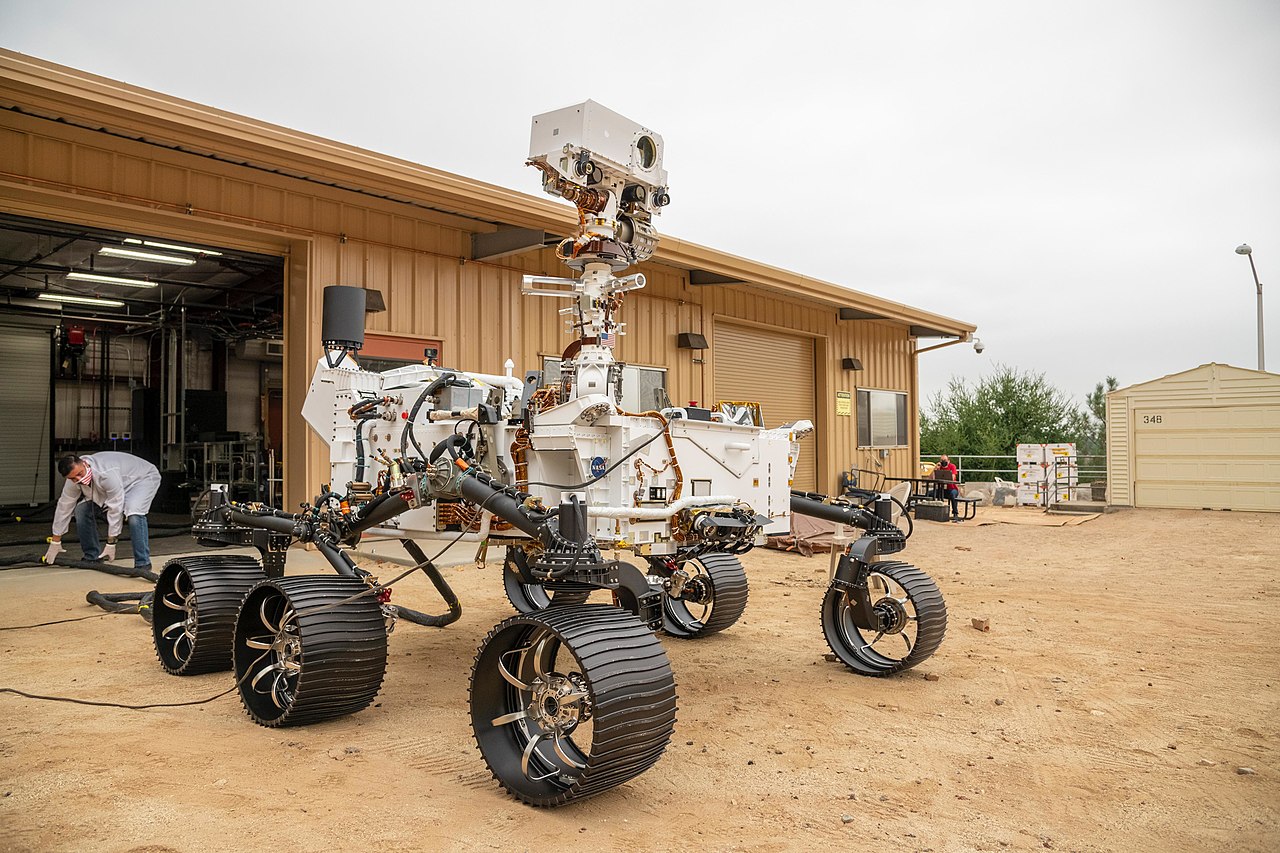
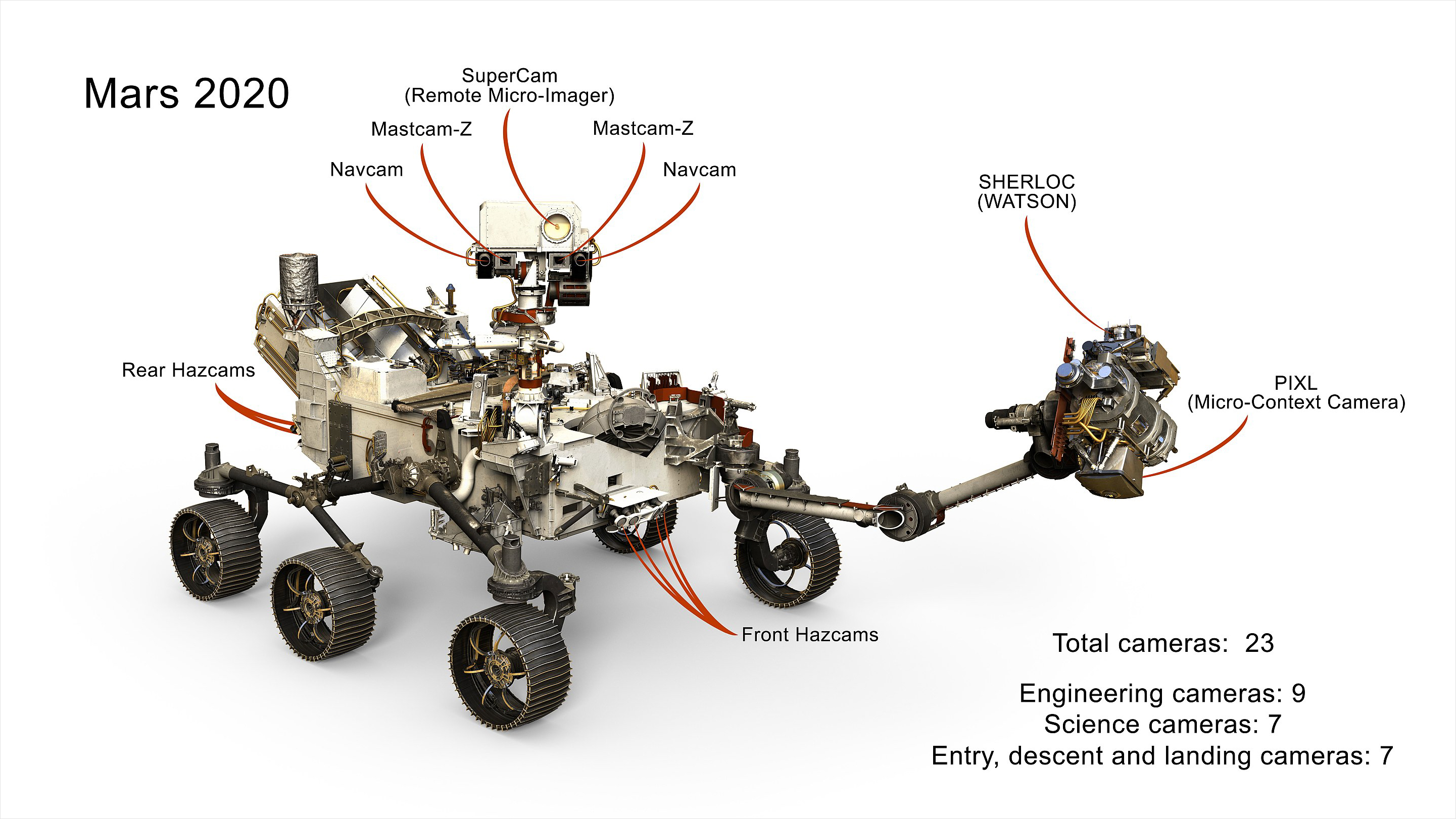
Although Perseverance has a similar design to its predecessor, Curiosity, it has been moderately improved: it carries 7 primary payload instruments, 23 cameras (9 engineering, 7 science, and 7 entry, descent, and landing) and 2 microphones.
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Two scientific instruments installed on the rover’s robotic arm allow it to analyze the chemical, mineral, physical and organic characteristics of Martian rocks and determine the best locations to collect samples, while high-resolution imaging and three types of spectroscopy to characterize rocks and soil from a distance help Percy determine which rock targets to explore up close. The collected samples are then sealed in tubes and stored in the rover chassis to be retrieved by a future mission for in-depth analysis on Earth.
“The belly of the rover houses all the equipment and supplies needed to collect the samples. It contains a rotating drill carousel, which is a wheel containing different types of drill bits,” NASA explained.
“As the rover’s large arm extends and drills into the rock, the rover’s belly houses a small robotic arm that functions as a ‘lab assistant’ for the large arm. The small arm retrieves and moves new sample tubes to the drill, and transfers the filled sample containers to a space where they are sealed and stored,” they added.
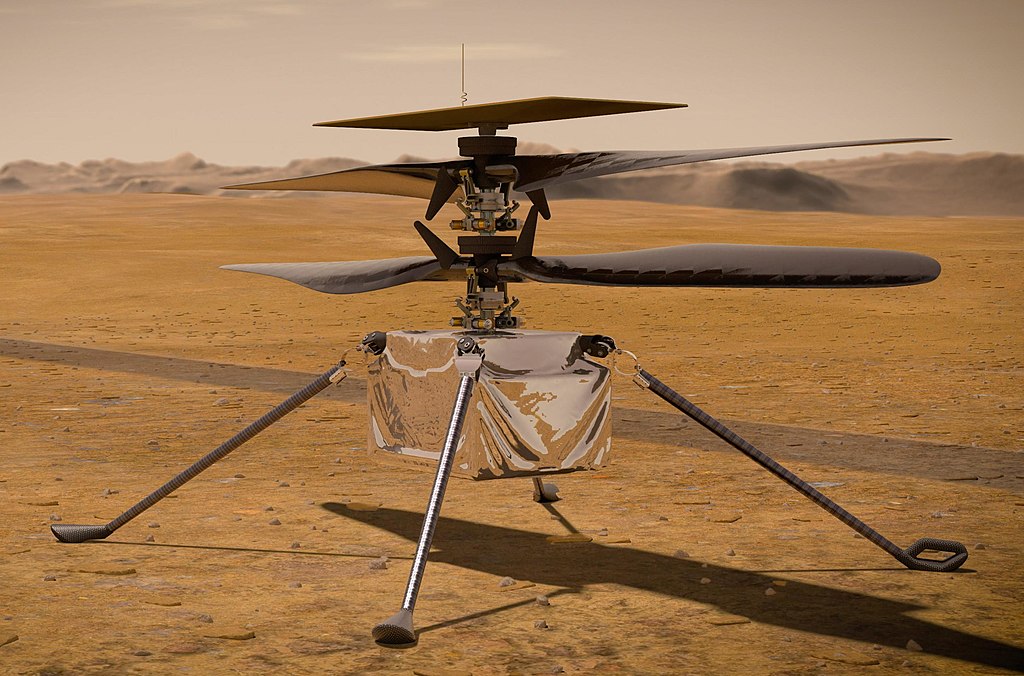
The rover also carried the mini-helicopter called Ingenuity, an experimental technology testbed that made the first powered aircraft flight on another planet. However, on January 18, 2024, it made its 72nd and final flight and, due to damage to its rotor blades during landing, it had to be retired by NASA.
Analysis by the rover’s SuperCam and Mastcam-Z instruments indicates that Atoko Point is composed of the minerals pyroxene and feldspar.
Photo credits: ESA
Photo credits: SETI Institute
Photo credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Over the years, 6 rovers have operated on Mars: Sojourner, Spirit and Opportunity, Curiosity and Perseverance (Percy), managed by NASA’s American Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and Zhurong, managed by the China National Space Administration.
Regardless of the technical differences, they have all been focused on the 4 main long-term objectives of the Mars exploration program:
- to discover if life ever existed on Mars;
- characterize the climate of the red planet;
- characterize the geology of Mars;
- prepare for human exploration.
Although Perseverance was designed to last only a few years on Mars, it is very likely that it will outlast predictions because, for example, its twin, Curiosity, is still going strong after nearly 11 years of roaming.
The main reason for its long lifespan could be that these two rovers use a nuclear power source instead of solar panels which can stop working when covered with dust or when the sun is dimmed during storm season of dust.
Yet once the mission is complete, Percy will not return to Earth, as to date there is no known technology to revive the rover.
Image credits: NASA
Image credits: NASA
Photo credits: NASA
Since 2021, NASA’s Perseverance rover has made remarkable discoveries about the Red Planet’s surface, including its volcanic history, climate, and the role of water in Jezero Crater.
While early rovers focused on geology and understanding Mars’ environment, Percy is looking for signs of past life and the recent discovery of Atoko Point can certainly provide some clues.
[ad_2]
Source link